Building Information Modelling (BIM) has changed how buildings and infrastructure are designed, built, and managed. It brings together 3D modelling, data management, and teamwork to make construction more efficient, reduce mistakes, and improve project quality. By using a shared, data-rich model, teams can make better decisions, reduce waste, and keep projects on track.
In this article, you’ll learn the key aspects of BIM process design, the main components of BIM, and how to set up an effective BIM process. In addition, you’ll explore ways to overcome common challenges and best practices to improve workflows.
Understanding the BIM Process in Design

The BIM process in design uses digital tools and 3D models to plan and manage construction projects. It creates a detailed virtual model of a building or infrastructure, including its size, materials, systems, and performance.
This enables architects, engineers, and contractors to collaborate effectively in a shared space, improving coordination and reducing mistakes. BIM also makes it easier to visualise designs, plan construction steps, and use resources efficiently, making it an essential tool in modern construction.
A well-structured BIM process plays a crucial role in the design phase, ensuring accuracy, collaboration, and efficiency from the very beginning. It goes beyond traditional drafting by integrating data-rich models that support informed decision-making. To fully grasp its impact, it’s important to understand its purpose and how it shapes the design workflow.
Purpose of the BIM Process in Design
The BIM process transforms how construction projects are designed, built, and managed. It creates a detailed digital model that represents both the physical structure and how it functions. This model helps everyone involved—architects, engineers, contractors, and clients—work together smoothly.
BIM improves accuracy, reduces mistakes, and makes better use of materials and resources. It also ensures the design meets performance standards and sustainability goals, leading to smarter, more efficient construction.
The BIM process in design helps improve how projects are planned and built through:
- Better Teamwork: Everyone involved, like architects, engineers, contractors, and clients, can work together in a shared digital space.
- More Efficiency: It speeds up design and construction by reducing manual work and avoiding mistakes.
- Higher Accuracy: The digital model ensures precise planning, lowering the risk of costly errors.
- Smart Use of Resources: Materials and resources are managed efficiently, reducing waste and extra costs.
- Testing Before Building: Simulations allow teams to explore different designs and fix issues before construction starts.
- Faster Decisions: Instant access to project data helps teams make informed choices quickly.
- Eco-Friendly Design: BIM helps assess energy use and materials, supporting sustainable building practices.
- Long-Term Maintenance: The detailed model remains helpful in managing the building throughout its life.
Understanding the purpose of the BIM process in design highlights its role in improving collaboration, efficiency, and accuracy. However, to see how it all comes together, it’s important to break down the key components that drive this process.
Also read: Understanding LOD in BIM: Definition, Differences, Levels, and Types.
Key Components of the BIM Process in Design
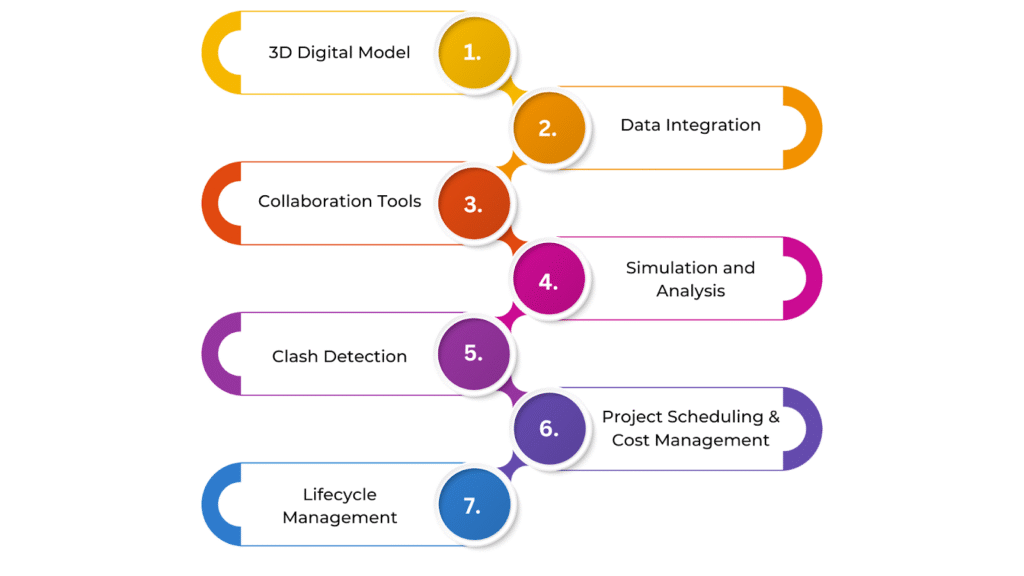
The key parts of the BIM process in design help teams work together smoothly, improve accuracy, and make projects more efficient. These include creating a 3D digital model, adding essential details about materials, systems, and performance, and using advanced tools for analysis.
BIM also depends on teamwork, allowing architects, engineers, and contractors to easily share and update information throughout the project. Below are the key components of the BIM process in design:
3D Digital Model
A 3D digital model is the foundation of the BIM process. It gives a virtual view of the building, showing its physical shape and layout. Unlike 2D drawings, a 3D model helps visualise how different building parts fit together in real space.
It includes details about the building’s architecture, structure, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) systems, making it easier for teams to understand the design as a whole.
Data Integration
BIM combines different types of data in one model, such as materials, construction methods, and product details. This data helps in making informed decisions at every stage of the project.
For example, information about energy use, HVAC systems, or building materials can be added to assess sustainability and efficiency. Instead of just being a visual tool, the BIM model becomes a source of valuable and actionable information.
Collaboration Tools
BIM makes teamwork easier by allowing architects, engineers, contractors, and clients to work on the same model in real time. Cloud-based platforms let everyone access, update, and share information instantly.
This minimises miscommunication, keeps all team members aligned, enhances productivity, and helps prevent conflicts later in the project.
Simulation and Analysis
BIM tools can simulate how a building will perform before construction begins. These simulations cover energy use, lighting, ventilation, and more. For example, an energy simulation can help optimise HVAC systems for better efficiency or identify areas that need extra insulation.
By analysing different scenarios, designers can improve building performance, reduce costs, and make sustainable choices.
Clash Detection
One of BIM’s biggest benefits is its early detection of design conflicts. It can automatically spot clashes, such as a duct interfering with a structural beam or plumbing crossing electrical wiring. Identifying these issues before construction prevents costly delays and rework, ensuring all systems fit together correctly.
Project Scheduling and Cost Management
BIM connects design with time (4D) and cost (5D) data, helping teams plan construction schedules and budgets more effectively. This allows project managers to allocate resources efficiently and spot potential delays or cost overruns in advance.
For example, BIM can track material deliveries and coordinate labour schedules to keep everything on track.
Lifecycle Management
BIM isn’t just useful for design and construction; it also helps with long-term building management. Once the project is completed, the model can store important details about materials, systems, and equipment for maintenance.
For instance, it can track when equipment was last serviced, monitor warranties, and provide updates on building components. This helps reduce maintenance costs and ensures smooth operations throughout the building’s life.
A well-structured BIM process ensures smooth collaboration, reduces errors, and enhances project efficiency. To achieve these benefits, it’s important to follow a clear, step-by-step approach.
Ready to simplify your projects and achieve the benefits?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for Revit Architectural and Structural Solutions. They coordinate with your team to develop, record, and streamline the BIM Revit Model, along with the sheets, Bill of Quantities, Bill of Materials, and clash coordination.
Steps in Designing an Effective BIM Process

Creating a successful BIM (Building Information Modelling) process takes careful planning to ensure smooth teamwork, accuracy, and efficiency throughout the project. The key steps include setting clear project goals, choosing the right software, building a collaborative work environment, and ensuring data is integrated at every design and construction stage.
By following these steps, teams can use BIM to improve workflows, catch issues early, and complete sustainable, high-quality projects on schedule and within budget. Below are the steps for designing an effective BIM process:
- Define Project Goals and Objectives
Before starting with BIM, it’s important to set clear goals for the project. These goals should match the overall vision, whether it’s improving teamwork, reducing costs, increasing accuracy, or ensuring sustainability. Having well-defined objectives helps guide decisions and keeps the team focused on the desired outcomes.
- Select the Right BIM Software and Tools
Choosing the right BIM software is key to a successful project. The software should support the project’s needs, such as 3D modelling, collaboration, simulation, and analysis.
It should also work well with other tools that architects, engineers, and contractors use. Popular BIM software includes Revit, ArchiCAD, and Navisworks, each offering different strengths based on project requirements.
- Develop a Collaborative Environment
BIM works best when everyone involved in the project can share and update information easily. Setting up clear rules for data sharing, version control, and communication helps keep the project organised. Cloud-based platforms allow real-time updates, reducing the risk of miscommunication and mistakes.
- Create a BIM Execution Plan (BEP)
A BIM Execution Plan outlines how the BIM process will be managed throughout the project. It includes guidelines for data management, modelling standards, collaboration rules, and software usage. A well-structured BEP ensures that all team members understand their roles and responsibilities, keeping the process smooth from start to finish.
- Establish Clear Standards and Protocols
Setting consistent standards for modelling, data entry, and file management helps avoid confusion. Clear protocols for naming files, organising data, and maintaining model accuracy ensure that everyone follows the same workflow, making collaboration easier and reducing errors.
- Integrate Project Data and Systems
BIM is most effective when it combines information from different sources, such as architectural, structural, MEP-F, and construction schedules. A unified model improves coordination and helps identify potential issues early. BIM can also be connected with project and cost management software to ensure smooth data flow.
- Implement Simulation and Analysis Tools
BIM includes powerful tools that can simulate how a building will perform before construction begins. These tools help assess energy efficiency, structural stability, and other critical factors. Running these simulations ensures that the building meets performance standards and avoids problems later in the project.
- Perform Regular Reviews and Clash Detection
Regular model reviews and clash detection help keep the design error-free. Identifying conflicts between different systems—such as pipes clashing with structural beams—before construction begins can prevent costly mistakes and delays.
- Manage Construction and Handover with BIM
BIM remains useful even after the design phase. It can track progress, manage resources, and monitor schedules during construction. Once the project is finished, the BIM model can be used for as-built documentation and facility management, helping owners with maintenance, repairs, and upgrades.
- Evaluate and Optimise the BIM Process
After the project is completed, reviewing the BIM process helps identify areas for improvement. Learning from past projects can lead to better data integration, improved teamwork, and a more efficient BIM workflow in future projects. Continuous improvement ensures that BIM remains a valuable tool for better project management and execution.
Even with a well-planned BIM process, challenges can arise at various stages, from coordination issues to data management complexities.
Challenges & Solutions to the BIM Process in Design
The BIM process has transformed how buildings are designed and constructed however, using BIM comes with challenges. These can include technical issues like software compatibility and data management, as well as teamwork challenges such as communication gaps and the need for skilled professionals.
Despite these obstacles, the right strategies and tools can help teams successfully adopt and implement BIM. Below are the challenges and solutions to the BIM process in design:
| Challenges | Solutions |
| Software Compatibility Issues | Choose BIM software with strong interoperability across different platforms.Use file formats like IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) to ensure compatibility. |
| Data Management and Integration | Implement centralised data management systems to store and manage project data.Use cloud-based platforms for easy access and version control. |
| Lack of Skilled Personnel | Provide regular training and certifications for team members.Hire BIM specialists or consultants to bridge knowledge gaps. |
| Collaboration Barriers Between Teams | Establish clear communication protocols and define roles early on.Use cloud-based collaboration tools to ensure real-time updates and transparency. |
| Model Accuracy and Data Quality | Set up stringent modelling standards and guidelines for all team members.Conduct regular quality checks and audits throughout the project. |
| High Initial Costs | Start with smaller-scale projects to demonstrate BIM’s ROI.Look for BIM software with flexible pricing options or subscription models. |
| Resistance to Change from Traditional Methods | Educate stakeholders on BIM’s long-term benefits.Showcase successful BIM case studies to highlight its effectiveness and efficiency. |
| Clash Detection and Conflict Resolution | Use automated clash detection tools integrated with BIM software to identify and resolve issues early.Schedule regular model review meetings to address clashes. |
| Complexity in Handling Large Projects | Break the project into smaller, manageable components or phases.Implement strong project management practices to maintain clarity and focus. |
| Integration with Existing Systems | Ensure BIM models are compatible with existing enterprise systems (e.g., ERP, CMMS).Develop custom interfaces or APIs to integrate with current software. |
Overcoming challenges in the BIM process requires more than just reactive solutions—it calls for a proactive approach rooted in industry best practices.
Best Practices for Successful BIM Process in Design
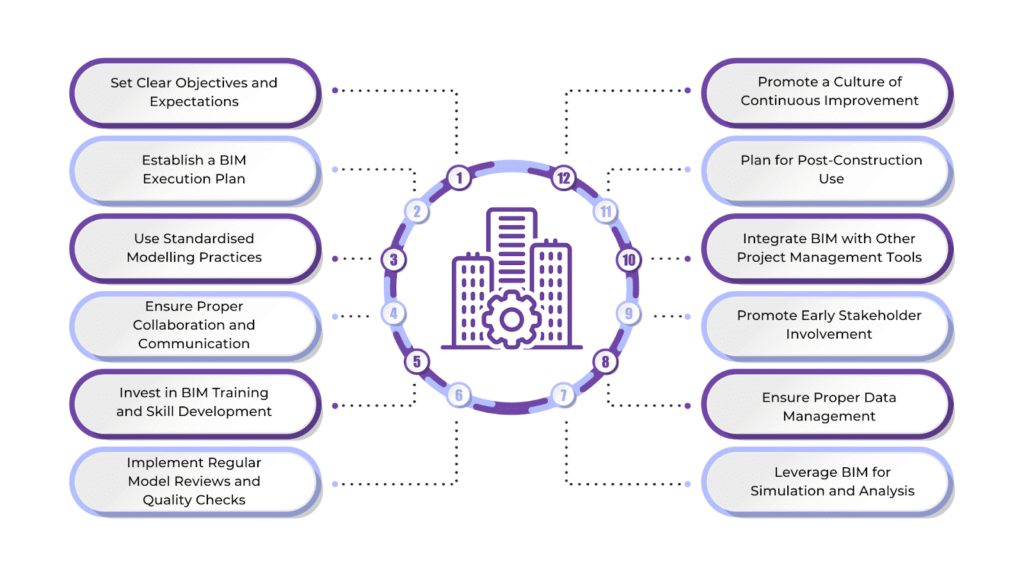
If you want to use BIM successfully in design, it requires best practices that improve teamwork, efficiency, and accuracy at every project stage. These include standardising workflows, improving communication, and using BIM tools.
Adopting these practices is key to ensuring smooth project execution and delivering great results. Below are the best practices for successful BIM process in design:
- Set Clear Objectives and Expectations: Start by defining the project’s goals and deliverables. Ensure all team members clearly understand the project scope, timeline, and how BIM will be used throughout the process.
- Establish a BIM Execution Plan (BEP): A BIM Execution Plan sets guidelines for workflows, software, and collaboration. It ensures all team members follow the same standards, keeping the project organised and efficient.
- Use Standardised Modelling Practices: Create clear rules for modelling, such as naming files, organising data, and structuring models. Standardised practices improve accuracy, prevent miscommunication, and make collaboration easier.
- Ensure Proper Collaboration and Communication: Encourage open communication among architects, engineers, contractors, and clients. Use cloud-based platforms for real-time updates and centralised access to the model, improving teamwork and reducing errors.
- Invest in BIM Training and Skill Development: Make sure team members are well-trained in BIM software and workflows. Continuous learning helps maintain high standards and ensures everyone can use the tools effectively.
- Implement Regular Model Reviews and Quality Checks: Conduct frequent model reviews to catch and fix errors early. Clash detection helps identify conflicts between different building systems (e.g., HVAC, electrical, and structural), reducing costly rework during construction.
- Leverage BIM for Simulation and Analysis: Use BIM tools to test building performance before construction begins. Simulations for energy efficiency, lighting, and airflow help optimise designs and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Ensure Proper Data Management: Store and organise project data on centralised, cloud-based platforms. This keeps all updates accessible to the team, reducing confusion and ensuring everyone works with the latest information.
- Promote Early Stakeholder Involvement: Involve key stakeholders, including owners and facility managers, early in the design phase. Their feedback ensures the model meets end-user needs and leads to better decision-making.
- Integrate BIM with Other Project Management Tools: Connect BIM with project management software for cost estimation, scheduling, and procurement. This integration helps track progress, control costs, and manage timelines more effectively.
- Plan for Post-Construction Use: BIM is valuable even after construction. Incorporate as-built information into the model to support maintenance, repairs, and future upgrades, ensuring long-term efficiency.
- Promote a Culture of Continuous Improvement: After the project is completed, review the BIM process to find areas for improvement. Gather feedback from all team members and apply lessons learned to enhance future projects.
BIM Supports GREEN EARTH.
Conclusion
BIM is changing how construction projects are planned and built. It improves efficiency, accuracy, and teamwork by using 3D models and real-time data. This helps teams work better together, avoid mistakes, and keep projects on track.
With new technologies like AI and automation, BIM will continue to evolve, making design and decision-making even smarter. To get the most out of BIM, teams should follow best practices, invest in training, and stay updated on the latest trends. Improving BIM workflows leads to better, more sustainable construction.
Are you looking for BIM solutions?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for the Architecture and Structure discipline. Their solutions help clients with better decision-making, cost-saving, efficient construction planning, and green earth initiatives.
You might also like: BIM Levels and Stages of Development Explained
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What are the 5 levels of BIM?
The five levels of BIM are:
- Level 0: No collaboration, 2D CAD drafting.
- Level 1: Basic 3D modelling with limited data sharing.
- Level 2: Collaborative 3D models with standardised formats.
- Level 3: Fully integrated, cloud-based collaboration.
- Level 4: Focus on sustainability and lifecycle management.
2. What are the 7 dimensions of BIM?
The seven dimensions of BIM include:
- 2D BIM: Traditional drawings and documentation.
- 3D BIM: Digital 3D modelling for visualisation.
- 4D BIM: Time and scheduling integration.
- 5D BIM: Cost estimation and budgeting.
- 6D BIM: Sustainability and energy analysis.
- 7D BIM: Facility management and maintenance.
- 8D BIM: Safety planning and risk mitigation.
3. Is BIM 3D or 4D?
BIM is both 3D and 4D. It starts with 3D modelling, which includes the building’s geometry and spatial relationships. When scheduling and time-related data are added, it becomes 4D BIM, enabling better project planning and construction sequencing.

