BIM is changing civil engineering by making project planning, design, and management more efficient. It helps cut planning time by up to 20% and reduces material costs by about 15%, making construction faster and more cost-effective.
At its core, BIM uses digital tools to create 3D models that bring all project data together. This makes teamwork easier, reduces mistakes, and improves workflows. Engineers use BIM for infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, tunnels and cities, relying on real-time updates to make better decisions at every stage of a project.
From start to finish, BIM helps teams work smoothly, avoid errors, and keep projects on time and within budget. In this article, you’ll learn about BIM’s role in civil engineering, its use, the challenges and solutions, essential tools, and key industry standards.
What is Building Information Modelling (BIM) in Civil Engineering?

Building Information Modelling (BIM) in civil engineering is a digital way of planning and managing construction projects. It creates a 3D model that includes both the physical structure and important details about how the building or infrastructure will function.
BIM helps visualise the entire project, covering design, construction, operation, and maintenance. It allows engineers, architects, and contractors to work together smoothly, reducing mistakes, improving coordination, and ensuring the project runs efficiently.
BIM allows teams to make better decisions, cut costs, and complete projects more effectively. By improving collaboration and reducing errors, BIM helps civil engineering projects run more smoothly.
Benefits of BIM in Civil Engineering Projects
BIM brings significant benefits to civil engineering projects, changing the way design, construction, and maintenance are handled. By using digital tools to create a detailed 3D model, BIM helps save costs, manage time better, and improve teamwork. It lets everyone involved see the project clearly, spot possible problems early, and make smart decisions before construction begins.
BIM helps in civil engineering projects through:
- Better Teamwork: BIM improves communication between architects, engineers, and contractors, reducing misunderstandings and conflicts.
- Cost Savings: By detecting issues early in the design phase, BIM helps avoid expensive changes and delays, keeping the project within budget.
- Time Efficiency: BIM simplifies planning and construction with detailed 3D models and accurate scheduling, shortening project timelines.
- Clear Visualisation: A 3D model provides a realistic view of the project, helping in better design decisions and a clearer understanding of the final structure.
- Fewer Errors and Risks: BIM detects design flaws and clashes before construction starts, reducing rework and costly mistakes.
- Sustainability: BIM promotes energy-efficient designs, better material use, and waste reduction, making projects more environmentally friendly.
- Better Facility Management: The data from BIM supports long-term maintenance and operations, benefiting building owners and managers.
- Higher Accuracy: Real-time data improves precision in design and construction, reducing errors and missing details.
- Organised Documentation: BIM automates documentation, ensuring all stakeholders have up-to-date, accurate project information.
- Improved Safety: BIM simulates construction processes and helps identify and prevent safety risks before work begins on-site.
With its many benefits, BIM has become a vital part of modern civil engineering. From design and planning to construction and maintenance, BIM is used in various ways to improve project outcomes.
How is BIM Used in Civil Engineering?
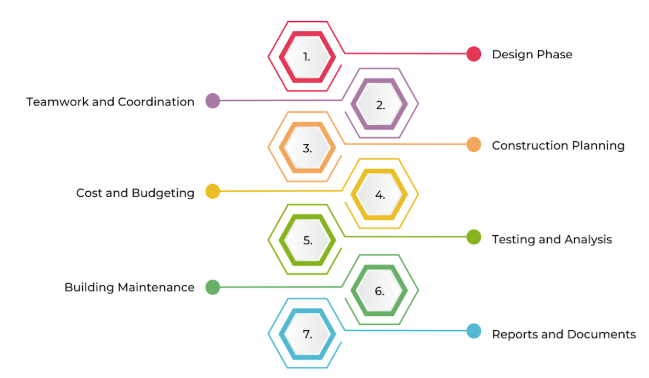
BIM is changing civil engineering by improving project planning, design accuracy, and construction efficiency. It allows engineers to create smart 3D models that combine data from different fields, making teamwork and decision-making easier.
BIM is used in civil engineering from the early design stage to project completion. Here’s how BIM is applied in civil engineering:
Design Phase
BIM helps create 3D models of buildings, roads, tunnels, and bridges, integrating architecture, structure, and MEPF (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing, Fire) systems to ensure everything fits together. Engineers can test different designs, visualise them, and make improvements before construction begins.
Teamwork and Coordination
BIM allows architects, engineers, contractors, and clients to work on the same model, making it easier to find and fix mistakes early, saving time and money. With real-time updates, communication improves, and project management becomes more efficient.
Construction Planning
BIM helps plan construction by creating 4D models that include steps, schedules, and sequencing. Contractors can visualise each stage, estimate materials, and track progress, improving efficiency and reducing delays while managing resources, costs, and changes in real time.
Cost and Budgeting
BIM provides accurate cost estimates for materials, labor, and equipment, ensuring better budgeting and preventing unexpected expenses. Since it updates automatically, any design changes are immediately reflected in cost calculations.
Testing and Analysis
Engineers use BIM to simulate energy use, building strength, and traffic flow, helping optimise safety, performance, and sustainability. They can refine designs for better efficiency by testing real-world conditions before construction.
Building Maintenance
Even after construction, BIM remains valuable by storing details on materials, equipment, and maintenance schedules. Building owners can use this data for repairs and upkeep, reducing long-term costs and ensuring smooth operations.
Reports and Documents
BIM automates the creation of detailed construction documents, minimising errors and keeping everyone updated. It also generates reports on project progress, costs, and key metrics, helping managers make informed decisions.
While BIM offers many advantages in civil engineering, its implementation comes with challenges.
Also read: A Guide to Building Information Modelling (BIM) Impact on Modern Construction Industry.
Challenges of Using BIM in Civil Engineering
Although BIM brings many benefits to civil engineering, it also comes with challenges like software compatibility issues, high initial costs, and the need for specialised training. However, these challenges can be managed with standardised data formats, proper training programmes, and cloud-based collaboration tools.
By tackling these obstacles, civil engineers can fully use BIM to improve project efficiency and develop better infrastructure. Below are the challenges of using BIM in civil engineering and the solutions for these challenges:
| Challenges | Solutions |
| High initial cost of implementation | Invest in training and software tools gradually to spread out costs.Consider adopting cloud-based BIM solutions to reduce upfront infrastructure investment. |
| Lack of skilled professionals | Offer training and certification programmes for employees.Partner with educational institutions to ensure the next generation of engineers is skilled in BIM. |
| Data management complexity | Use centralised BIM platforms to manage data and ensure all stakeholders can access real-time information.Implement robust data standards and workflows. |
| Software compatibility issues | Select BIM software with open standards that integrate well with other tools used by engineers, architects, and contractors.Ensure proper software training and collaboration. |
| Resistance to change in traditional practices | Educate stakeholders on the long-term benefits of BIM, including cost savings and improved project outcomes.Highlight successful case studies to gain buy-in. |
| Integration with existing systems | Plan for a phased integration of BIM with legacy systems, focusing on interoperability and gradual adoption across different project phases. |
| Data security concerns | Implement strong cybersecurity protocols for BIM data storage, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular system audits. |
| Coordination challenges among stakeholders | Use cloud-based BIM tools to ensure real-time access to models for all project participants.Establish clear communication protocols and set up regular coordination meetings. |
| Modelling accuracy and quality control | Implement strict quality control checks throughout the design and construction phases.Use automated tools within BIM software to detect potential design errors. |
| Ongoing maintenance and updates | Establish protocols for keeping BIM models updated throughout the life of the project.Ensure that future upgrades to the model are integrated smoothly with the initial data. |
Addressing BIM challenges is easier with the right technology. Various software tools help civil engineers simplify workflows, improve collaboration, and enhance project accuracy.
Ready to simplify your projects and achieve the benefits?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for Revit Architectural and Structural Solutions. They coordinate with your team to develop, record, and streamline the BIM Revit Model, along with the sheets, Bill of Quantities, Bill of Materials, and clash coordination.
BIM Software & Tools in Civil Engineering
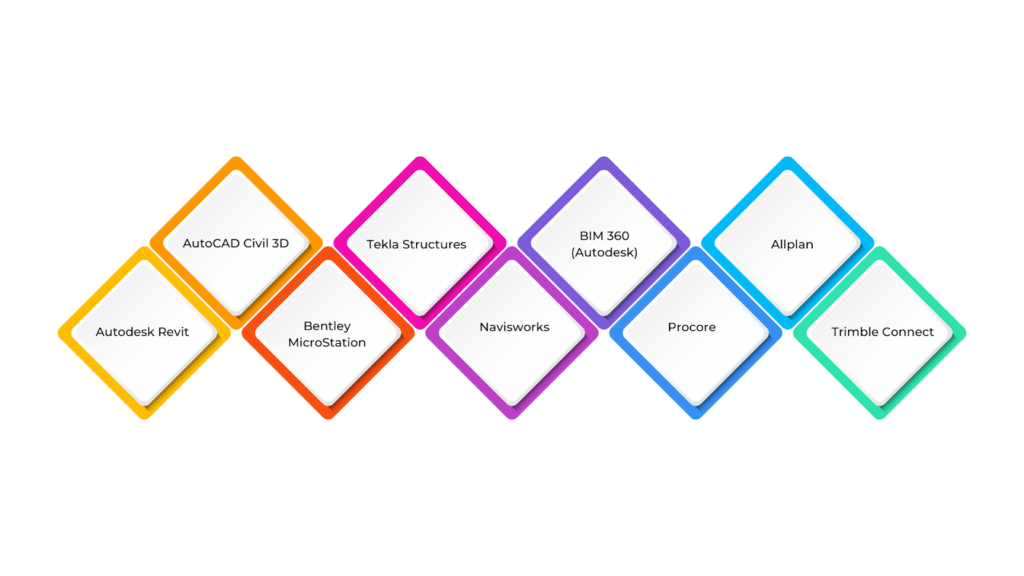
BIM software and tools are changing how civil engineering projects are designed, built, and maintained. They provide advanced digital solutions that make the entire process smoother and more efficient. With shared 3D models, engineers, architects, and contractors can work together quickly, improving accuracy and teamwork.
BIM tools help with everything from structural analysis to project scheduling, making it easier to make informed decisions, reduce mistakes, and use resources wisely. Below are the top BIM software and tools used in civil engineering:
- Autodesk Revit
This powerful BIM tool is used for designing buildings, including structural, architectural, and MEP systems. It provides 3D modelling, design visualisation, and simulation features, allowing teams to collaborate efficiently. Revit also supports data-rich models that help with cost estimation, scheduling, and construction planning.
- AutoCAD Civil 3D
This is designed specifically for civil engineering projects such as roads, highways, and land development. It offers tools for grading, drainage design, and terrain modelling, making it easier to analyse and design civil infrastructure with accuracy.
- Bentley MicroStation
This is widely used for infrastructure projects like bridges, tunnels, roads, and utilities. It enables engineers to create 3D models, visualise designs, and generate precise documentation. MicroStation also integrates well with other Bentley tools, ensuring a smooth workflow throughout different project stages.
- Tekla Structures
This focuses on structural engineering and helps engineers design detailed models for buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure. It offers advanced steel and concrete detailing tools, construction planning, and material management, making it ideal for complex structural projects.
- Navisworks
This is primarily used for project coordination and clash detection. It combines models from different disciplines to identify conflicts before construction begins, reducing costly errors. It also allows project teams to visualise and simulate construction processes for better planning.
- BIM 360 (Autodesk)
This is a cloud-based platform that helps manage construction projects and documentation. It allows teams to work together instantly, track project progress, and manage documents efficiently. This tool is handy for large-scale projects requiring seamless coordination.
- Procore
This is a construction management software that integrates with BIM to streamline workflows. It helps teams manage budgeting, scheduling, and communication while providing real-time updates using BIM models to ensure smooth project execution.
- Allplan
This is a BIM tool that supports both architectural and engineering design. It offers detailed modelling, construction planning, and collaborative features, making it a reliable solution for improving project efficiency and accuracy.
- Trimble Connect
This is a collaboration platform that connects different BIM tools, enabling teams to share files and coordinate projects more effectively. It provides real-time access to 3D models, documentation, and schedules, ensuring all stakeholders stay updated throughout construction.
Using the right BIM software is crucial, but following industry standards and regulations is also important.
BIM Standards and Regulations across Australia and New Zealand
Australia and New Zealand have set BIM standards and regulations to ensure consistency and teamwork in the construction and infrastructure industries. These guidelines help improve project collaboration and efficiency, especially in government-funded civil engineering and construction projects.
BIM Standards and Regulations in Australia
In Australia, the National BIM Initiative provides a clear framework for using BIM software. A handbook guides professionals on creating and managing BIM models, with a strong focus on teamwork and information sharing.
Additionally, the National Australian Built Environment Rating System (NABERS) uses BIM data to measure the environmental performance of buildings. This ensures sustainable and energy-efficient designs.
The Australian Government also has a BIM Strategic Framework to support BIM adoption in public projects. This framework improves asset management and makes procurement processes smoother.
BIM Standards and Regulations in New Zealand
New Zealand follows BIM standards to enhance infrastructure projects, particularly in transportation. The New Zealand Transport Agency (NZTA) has a BIM Design Guidebook that helps integrate BIM into transport-related projects.
To accelerate BIM adoption, the BIM Acceleration Committee focuses on better collaboration, data sharing, and system compatibility across the construction sector. New Zealand’s BIM guidelines align with global standards, making it easier to work with international partners.
The ‘Building Information Modelling Collaboration Tool Requirements for Government Agencies’ outlines the mandatory BIM deliverables for government-funded projects. This ensures that BIM is used effectively in public sector projects.
Australia and New Zealand are committed to improving construction efficiency, sustainability, and collaboration through BIM. Their regulations and standards help ensure projects run smoothly while meeting high industry standards.
BIM Supports GREEN EARTH.
Conclusion
BIM has changed civil engineering by making project planning, design, construction, and maintenance more efficient. It helps teams work together, reduces mistakes, and improves quality, safety, and sustainability.
In the future, BIM will become even smarter with technologies like AI, machine learning, and cloud computing. These advancements will improve project management and make construction faster, more accurate, and cost-effective. As more companies adopt BIM, it will keep driving the future of civil engineering and infrastructure growth.
Are you looking for BIM solutions?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for the Architecture and Structure discipline. Their solutions help clients with better decision-making, cost-saving, efficient construction planning, and green earth initiatives.
You might also like: BIM Levels and Stages of Development Explained.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Can a civil engineer be a BIM engineer?
Yes, a civil engineer can become a BIM engineer by learning BIM software like Revit, Navisworks, or Tekla. BIM engineering focuses on creating and managing digital models of buildings and infrastructure, which aligns well with a civil engineer’s skills in design, planning, and construction.
2. Does AutoCAD have BIM?
AutoCAD itself is not a BIM tool, but Autodesk offers AutoCAD Architecture and Civil 3D, which have some BIM-related features. However, full BIM capabilities are found in software like Revit, which is designed specifically for building information modelling.
3. Is BIM only 3D?
No, BIM is more than just 3D modelling. It includes additional dimensions like 4D (time/scheduling), 5D (cost estimation), 6D (sustainability), and 7D (facility management).

