Structural drawings play a key role in construction, acting as a detailed blueprint for a building’s framework. They focus on important structural elements like foundations, beams, columns, and reinforcements that provide strength and stability and stability to the structure.
These drawings also ensure that construction meets safety standards and building codes. By providing clear guidelines, they help builders work accurately, reducing mistakes and improving efficiency.
In this article, you’ll learn what structural drawings are, what information they include, how to design them, and how to read them for successful construction.
What are Structural Drawings?
Structural drawings are detailed plans that show how a building or structure will be built. They include essential information about the size, shape, and materials of key parts like the foundation, walls, beams, and columns. These drawings help builders, engineers, and contractors follow the correct methods to ensure the structure is strong, safe and meets building codes.
Structural drawings include different views, such as floor plans, side views (elevations), and cross-sections, to give a clear picture of the design. This helps everyone involved in the construction process understand how the structure should be built.
While structural drawings focus on the framework and support of a building, they are often used alongside architectural drawings.
Difference Between Architectural and Structural Drawings
Architectural and structural drawings play different but connected roles in construction. Architectural drawings focus on the building’s layout, appearance, and function. They show plans,, elevations, and materials to create a visually appealing and practical space.
Structural drawings, on the other hand, define the building’s support system. They represent the details of load-bearing elements like beams, columns, and foundations to ensure stability and strength. While architects shape the look and usability of a building, structural engineers make sure it stands firm.
Understanding both helps keep construction smooth, avoids conflicts, and ensures a well-coordinated project.
Below are the differences between architectural and structural drawings:
| Aspect | Architectural Drawings | Structural Drawings |
| Purpose | Focus on the design, aesthetics, and layout of the building or structure. | Focus on the structural integrity, strength, and support of the building. |
| Content | Includes floor plans, elevations, sections, and other architectural details such as windows, doors, and finishes. | Includes details about the foundation, columns, beams, load-bearing walls, and other structural components. |
| Responsibility | Created by architects, detailing the building’s overall look and functionality. | Created by structural engineers, detailing how the structure will support loads and resist forces. |
| Main Focus | Functionality, aesthetics, and spatial arrangement. | Load-bearing capacity, safety, and stability of the structure. |
| Materials | Specifies non-structural materials like finishes, cladding, and furniture layout. | Specifies structural materials like concrete, steel, wood, and reinforcements. |
| Scale | Typically drawn at a smaller scale to show detailed layouts and finishes. | Drawn at a larger scale to show detailed measurements and structural components. |
| Audience | Architects, interior designers, and clients. | Engineers, contractors, and construction teams. |
| Viewpoint | Primarily top-down, showing the layout of rooms, walls, windows, etc. | Often includes detailed cross-sections, elevations, and specific dimensions for construction. |
Understanding how structural drawings differ from architectural drawings helps clarify their specific construction roles. While architectural drawings focus on the building’s appearance and layout, structural drawings ensure it has the necessary strength and stability.
Benefits of Structural Drawings
Structural drawings are important for ensuring a building is safe, strong, and long-lasting. They give clear instructions on key support elements like foundations, beams, and columns, helping engineers and builders create a sturdy structure.
Accurate measurements and details help different teams work together smoothly, cut down on expensive changes, and keep construction on track. Below are the benefits of structural drawings:
- Ensures Safety: Provides a clear design to ensure the building can handle weight and forces, preventing collapses or failures.
- Guides Construction: Acts as a detailed blueprint for builders, showing how each structural part should be built.
- Follows Building Codes: Ensures the structure meets all safety rules and legal requirements, avoiding issues later.
- Saves Costs: Helps estimate materials accurately, reducing waste and preventing expensive mistakes.
- Improves Teamwork: Helps architects, engineers, and builders collaborate smoothly, keeping everyone on the same page.
- Supports Structural Analysis: Helps engineers test the design for strength and stability before construction starts.
- Prevents Mistakes: Identifies weak points or design problems early, reducing risks during construction.
- Keeps Records for the Future: Serves as a helpful reference for renovations, repairs, or expansions.
- Speeds Up Approvals: Provides detailed technical information required to get construction permits quickly.
Structural drawings offer many advantages, from ensuring safety and compliance to improving efficiency on-site. Their detailed plans help construction teams work with accuracy and confidence. To fully understand their value, it’s essential to look at the specific types of information these drawings include.
Also read: Understanding Architectural Drawings: Types, Techniques & Tips.
Types of Information Included in Structural Drawings
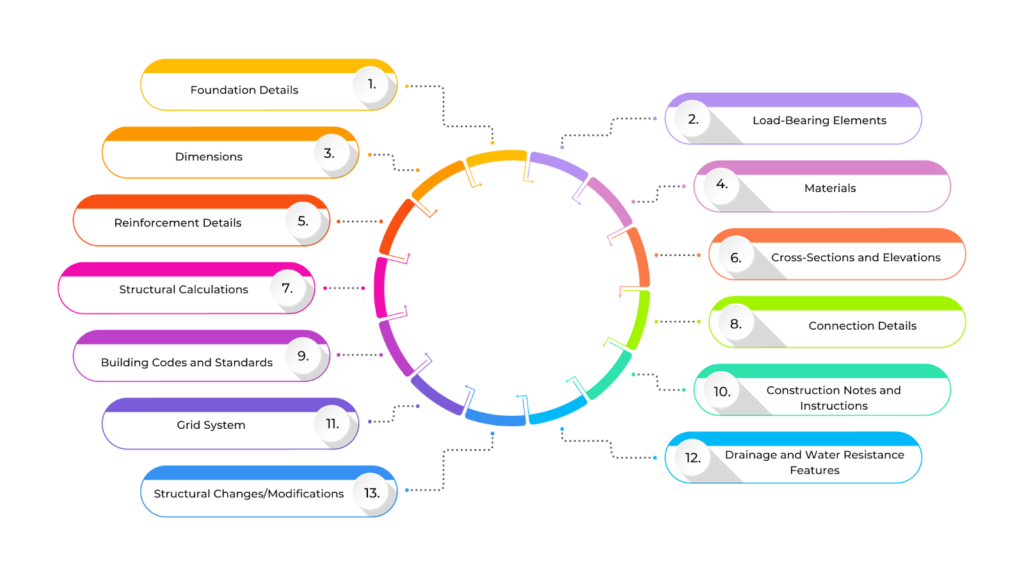
Structural drawings provide essential details needed to build a safe and strong structure. They show key support elements like beams, columns, and foundations, specifying their size, materials, and connections. These drawings also include reinforcement details, load calculations, and building methods to ensure everything meets safety standards. Below is the type of information included in structural drawings:
| Elements | Key Details |
| Foundation Details | Includes the type of foundation (slab, pier, footing), its size, and the materials used. |
| Load-Bearing Elements | Shows key structural parts like beams, columns, walls, and slabs, along with their size, material, and placement. |
| Dimensions | Provides exact measurements for all structural components, including their height, width, length, and spacing. |
| Materials | Specifies the materials used, such as concrete, steel, or wood, along with their quality and properties. |
| Reinforcement Details | Includes information on steel reinforcements (rebar) in concrete, such as size, spacing, and placement. |
| Cross-Sections and Elevations | Offers detailed vertical views to show how different parts of the structure connect and fit together. |
| Structural Calculations | Ensures the building can handle weight and pressure by including load capacities and safety factors. |
| Connection Details | Describes how different structural elements are joined using welds, bolts, or fasteners. |
| Building Codes and Standards | Lists the safety rules and legal codes the structure follows to meet regulations. |
| Construction Notes and Instructions | Provides special guidelines for building methods, sequencing, or unique requirements. |
| Grid System | Helps align and position structural elements correctly across different floors or sections. |
| Drainage and Water Resistance Features | Includes waterproofing and drainage solutions to protect the structure from water damage. |
| Structural Changes/Modifications | Notes any design adjustments made for specific site conditions or unique building needs. |
Structural drawings contain critical information about a building’s framework, including details on load-bearing elements, materials, and connections. However, having the right information is just one part of the process. The next step is understanding how to translate these details into a well-structured design.
Ready to simplify your projects and achieve the benefits?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for Revit Architectural and Structural Solutions. They coordinate with your team to develop, record, and streamline the BIM Revit Model, along with the sheets, Bill of Quantities, Bill of Materials, and clash coordination.
How to Design a Structural Drawing?
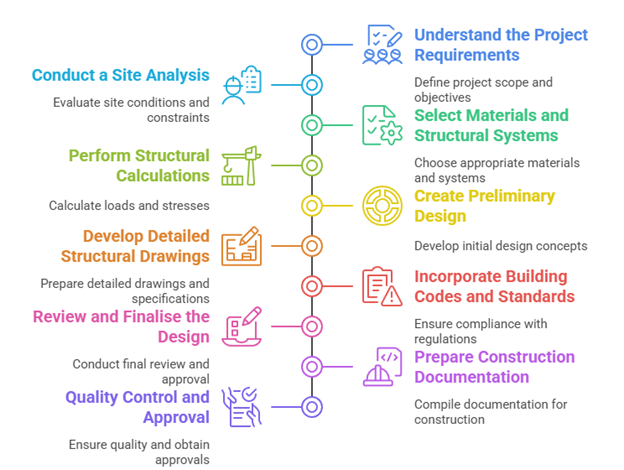
Creating a structural drawing requires careful planning to ensure a building is strong and stable. The process begins by reviewing the architectural plan and determining how much weight the structure needs to support.
Engineers then choose the right materials and design key elements like beams, columns, and foundations, calculating their sizes based on safety standards. A well-made structural drawing makes construction smoother, reduces risks, and ensures the building meets safety rules.
Below is a step-by-step approach to creating structural drawings:
- Understand the Project Requirements
This involves reviewing architectural drawings to study the building’s layout, dimensions, and design needs. It also includes consulting with stakeholders such as architects, clients, and other professionals to discuss project goals and limitations.
- Conduct a Site Analysis
This requires a site survey to gather information about soil conditions, terrain, and climate factors that may impact the structure. Identifying load conditions is also crucial, which means determining the expected weight the structure must support, including live loads, dead loads, wind, and seismic forces.
- Select Materials and Structural Systems
Choosing materials involves deciding on concrete, steel, wood, or a mix based on the project’s needs. Determining structural systems includes selecting the framework, such as beams, columns, slabs, or trusses.
- Perform Structural Calculations
Load calculations help analyse different loads. Stress and strength analysis checks how forces act on the structure and confirms that materials can handle them. The factor of safety is also considered to include a margin for unexpected stresses.
- Create Preliminary Design
This step includes sketching an initial design with a rough layout of structural components like beams, columns, and foundations. Setting up a grid system ensures proper alignment of structural elements.
- Develop Detailed Structural Drawings
This includes foundation details specifying the type, size, depth, and reinforcement. Columns, beams, and slabs are shown with detailed sections, including dimensions and material specifications.
Reinforcement details indicate the placement, size, and spacing of steel reinforcements (rebar). Cross-sections provide sectional views to illustrate how components fit together. Connection details define how parts are joined using welding, bolts, or other methods.
- Incorporate Building Codes and Standards
This involves following local, national, and international building codes and documenting compliance by referencing the necessary codes and standards in the drawings.
- Review and Finalise the Design
Reviewing and finalising the design involves collaboration with engineers to verify the design’s accuracy and feasibility. Revisions are made based on feedback.
- Prepare Construction Documentation
This includes adding construction notes that provide instructions for construction, including material details and step-by-step processes. Finalised structural drawings are then issued to contractors.
- Quality Control and Approval
Ensuring accuracy requires double-checking all measurements, calculations, and details. The approval process involves submitting the drawings for official approval before starting construction.
Designing a structural drawing is just one part of the process. Once the plans are created, they need to be understood and interpreted correctly to ensure smooth execution on-site.
How to Read Structural Drawings?
Reading structural drawings is essential for understanding how a building is designed and ensuring it is built correctly. These drawings use symbols, notes, and measurements to show key parts like beams, columns, foundations, and reinforcements.
To read them properly, it is necessary to understand the legend, scale, section details, and material specifications. By paying close attention to these details, contractors, engineers, and site workers can follow the design accurately, avoid mistakes, and ensure the building is safe and meets all requirements.
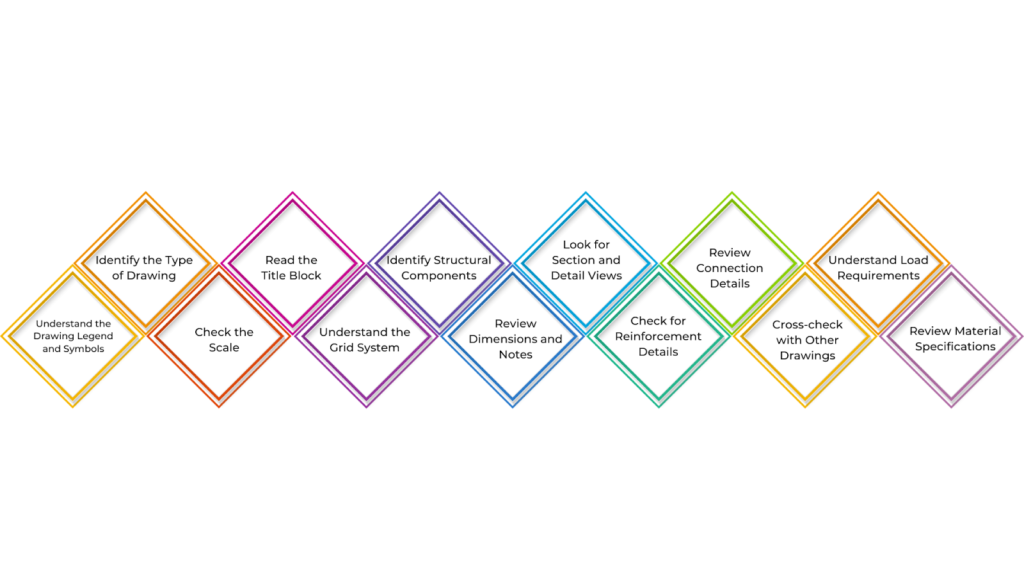
Reading structural drawings may seem complicated, but understanding key elements makes it easier. Here’s how to read structural drawings:
Understand the Drawing Legend and Symbols
Structural drawings use symbols to represent beams, columns, foundations, and reinforcements like rebar. The legend or key explains what these symbols and abbreviations mean, helping you read the drawing accurately.
Identify the Type of Drawing
Floor plans show the layout of structural elements on each floor, while elevations provide views from different angles, showing vertical dimensions. Sections offer a cut-through view of the structure to display how different parts connect. Detail drawings focus on specific components like joints or reinforcements.
Check the Scale
Structural drawings are scaled representations of real-life dimensions. For example, a 1:100 scale means that 1 unit on the drawing represents 100 units in reality. Always verify the dimensions based on the scale provided.
Read the Title Block
The title block contains important project details. Usually found in the bottom right corner, it includes the project name, drawing number, date, revision history, and the names of the architect and engineer. Always check for the latest revision to avoid outdated information.
Understand the Grid System
Grid lines, marked with letters and numbers, assist in placing structural elements correctly. The intersection of these lines, called grid points, helps locate beams, columns, and other components.
Identify Structural Components
Foundations include details about footing types, depth, and reinforcement. Beams and columns are load-bearing elements, with their sizes and materials clearly specified. Slabs, representing floors or ceilings, indicate thickness and material specifications. In addition, reinforcement details show the placement and spacing of steel bars in concrete elements.
Review Dimensions and Notes
Dimensions specify the size, length, and height of each component, often provided in millimetres or feet/inches. Construction notes offer important instructions on materials, methods, and standards to be followed.
Look for Section and Detail Views
Sections give a vertical slice of the structure, showing internal layouts, while detail views zoom in on specific joints, beams, or reinforcement areas for better understanding.
Check for Reinforcement Details
If the structure includes reinforced concrete, drawings specify the size, type, spacing, and layout of steel bars, ensuring proper strength and durability.
Review Connection Details
Structural drawings include specifications for bolts, welds, and joints, along with the required materials. Checking these ensures all components are securely connected as per design.
Cross-check with Other Drawings
Structural drawings should align with architectural plans to ensure the correct placement of elements. If other systems like electrical, plumbing, or HVAC are involved, verifying integration helps avoid conflicts.
Understand Load Requirements
Some structural drawings specify the loads the structure must support, including live loads, dead loads, wind, and seismic forces. Checking for safety margins ensures that the structure can handle expected stresses.
Review Material Specifications
The drawings indicate the required materials, such as concrete, steel, or wood, along with their grades. Using the right materials ensures the structure meets design and safety standards.
By following these steps, you can confidently read structural drawings, ensuring accurate construction and avoiding errors.
BIM Supports GREEN EARTH.
Conclusion
Structural drawings are essential for keeping a construction project safe and stable. Their detailed plans help create strong, secure, and efficient buildings. When construction teams understand these drawings correctly, they can help prevent costly mishaps and keep the project running smoothly.
These drawings provide critical details about materials, load-bearing elements, and connections, ensuring every part of the structure is built as intended. By learning how to read and use structural drawings, you can help build safe, long-lasting, and well-designed structures.
Are you looking for BIM solutions?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for the Architecture and Structure discipline. Their solutions help clients with better decision-making, cost-saving, efficient construction planning, and green earth initiatives.
You might also like: Detailed Drawings in Architectural Design: Types & Creation Process.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What are the five stages of structural design?
The five stages of structural design are as follows:
- Define project needs and explore structural options.
- Rough calculations and layouts to check feasibility.
- Precise calculations, material selection, and full drawings.
- Create official plans for builders and approvals.
- Build the structure and ensure it meets standards.
2. Who produces structural drawings?
Structural engineers create structural drawings and design the framework of buildings, ensuring safety and stability. Drafters or CAD technicians assist by turning designs into detailed blueprints. Architects may also contribute by coordinating the structure with the building’s overall design.
3. How to construct a structure?
To construct a structure, follow these steps:
- Define purpose, budget, and site conditions.
- Engineers and architects create structural plans.
- Excavate and lay the base for stability.
- Build walls, floors, and support systems.
- Add final details and check safety standards.

